Real vs. Nominal Returns

The nominal return is the amount of return attributed to an asset purely on a numerical basis. However, we know that increased inflation reduces the purchasing power of any nominal value over time.
The real return adjusts for this.
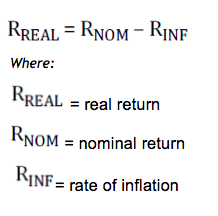
An example:
If an investment has generated a rate of return of 9% over the last year where inflation was 2% for the same time scale, what is the approximate real return?
-First we know that the nominal return is 9 and the rate of inflation is 2:
-We then place these figures directly into the formula:
-Therefore the investment has generated an approximate real return of 7%
Question - Use Your Note Taker To Jot Down Ideas / Calculations
If an investment has generated a rate of return of 8% over the last year where inflation was 3% for
the same time scale, what is the approximate real return?
a) 4%
b) 6%
c) 5%
d) 4.5%
C)
Deduct the rate of inflation (3%) from the nominal rate of return (8%). This gives us a real rate of
return of 5%.
- Further Study Text: Pages 165